CLDN6
(Claudin 6)是CLDN
(Claudin)家族的27个成员之一,也是组成细胞间紧密连接的重要分子。它位于染色体16p13.3上,分子量大约为20~40
kDa,包含四个跨膜结构域,两个细胞外ECL环(ECL1和ECL2),一个氨基端和一个羧基端。
CLDN6在细胞质的羧基端有四个跨膜结构域和一个pdz结合区。该CLDN可与信号蛋白和细胞骨架蛋白结合,参与细胞对外部和细胞内信号传递的应答。
CLDN6是唯一可能显示特异性的CLDN,因为它可以激活细胞粘附信号并调节核受体的活性。CLDN6在多种胚胎上皮中表达,诱导上皮细胞连接形成和极性,参与干细胞向上皮细胞的分化。研究发现,CLDN6在正常成人组织中未检测到表达,而在多种实体瘤组织如卵巢癌、睾丸癌、子宫内膜癌上呈高表达[1,3]。
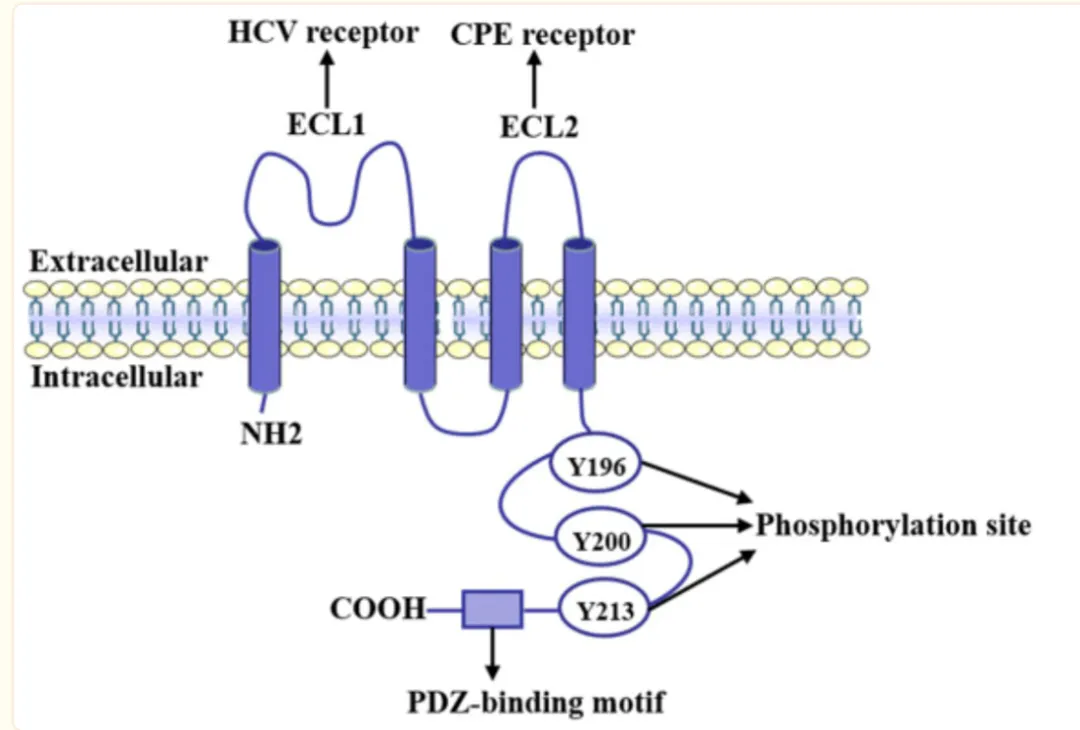
图1: CLDN6分子结构示意图
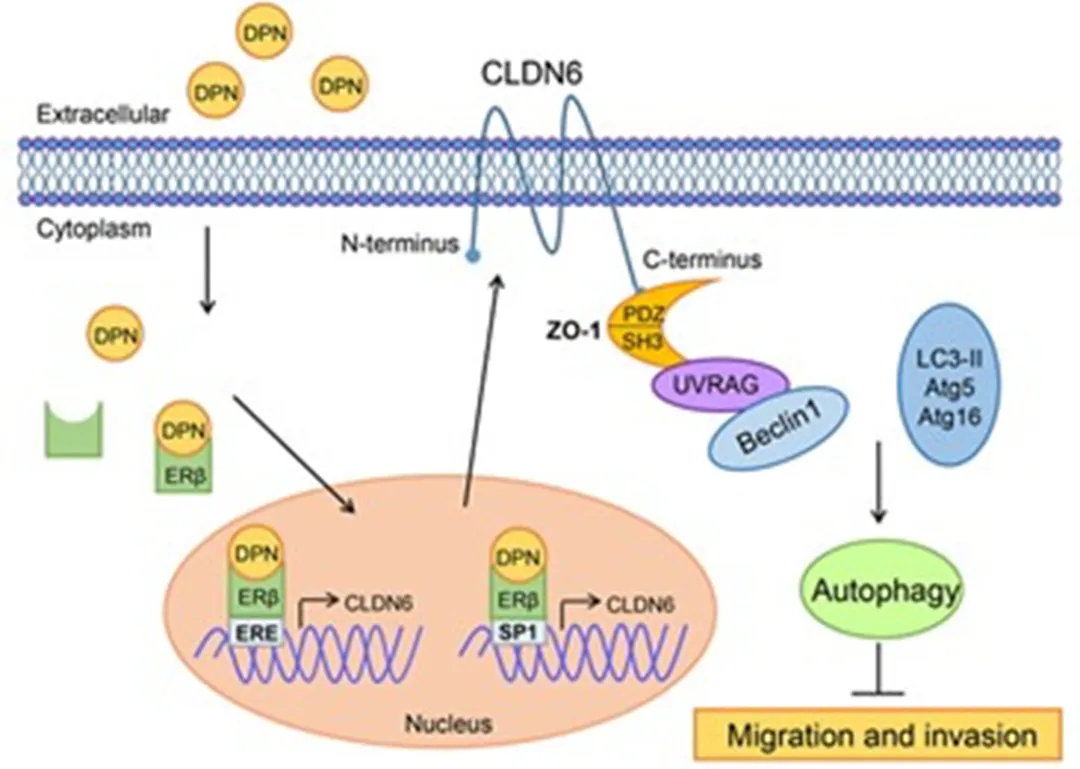
图2: CLDN6的激活及下游信息通路[1]
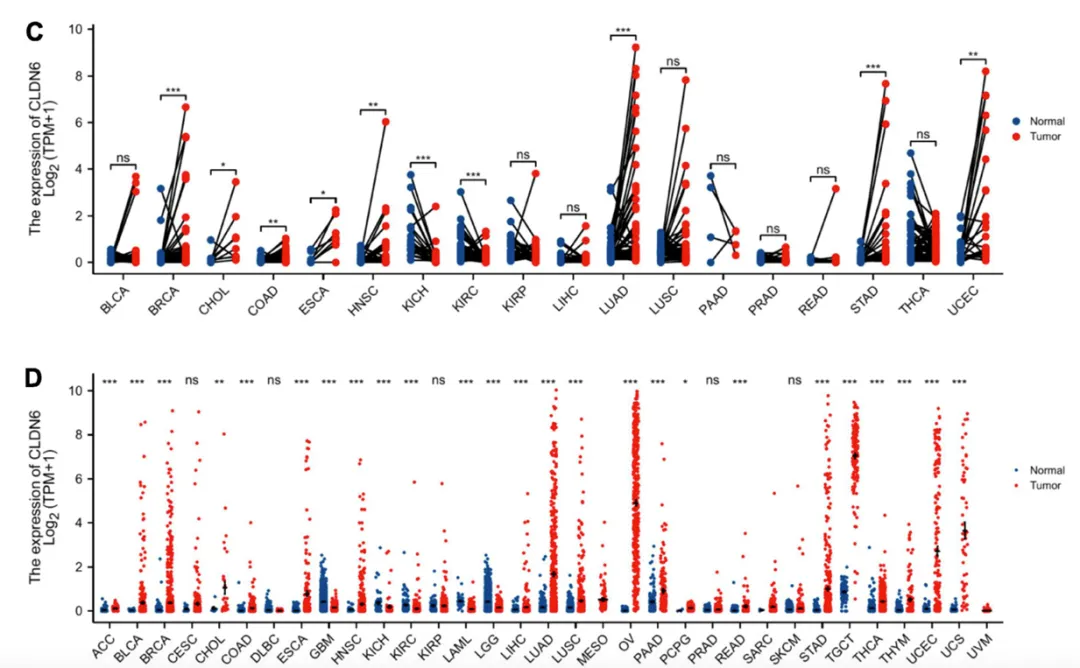
图3: CLDN6在不同癌症中以及正常组织中的表达 [2]
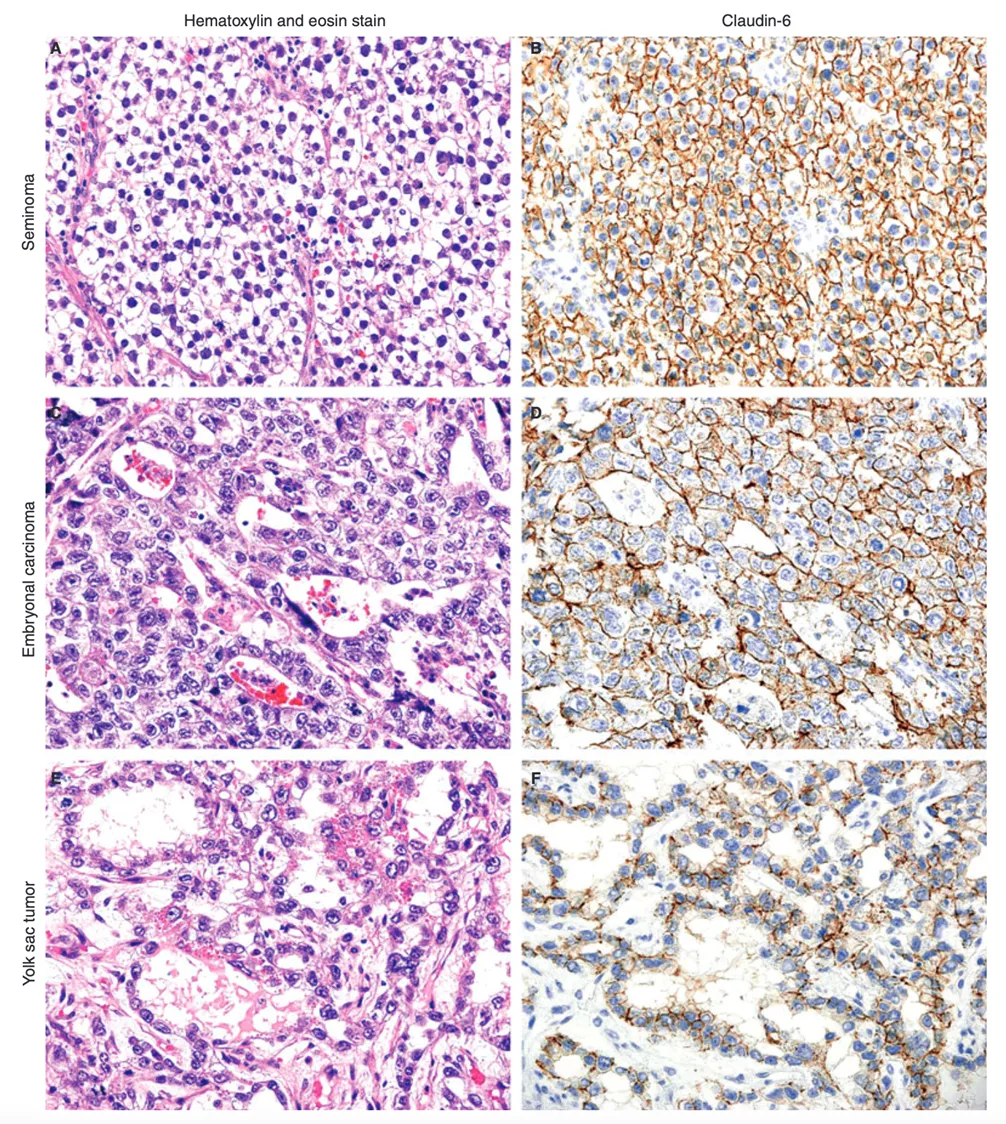
图4: CLDN6在不同生殖细胞癌中的表达[2]
精原细胞瘤(A、B)、胚胎癌(C、D)和卵黄囊瘤(E、F)的H&E染色以及claudin-6免疫组化染色。所有这些原始生殖细胞肿瘤的claudin-6膜染色均为中等(F)至高(B、D) 4+。
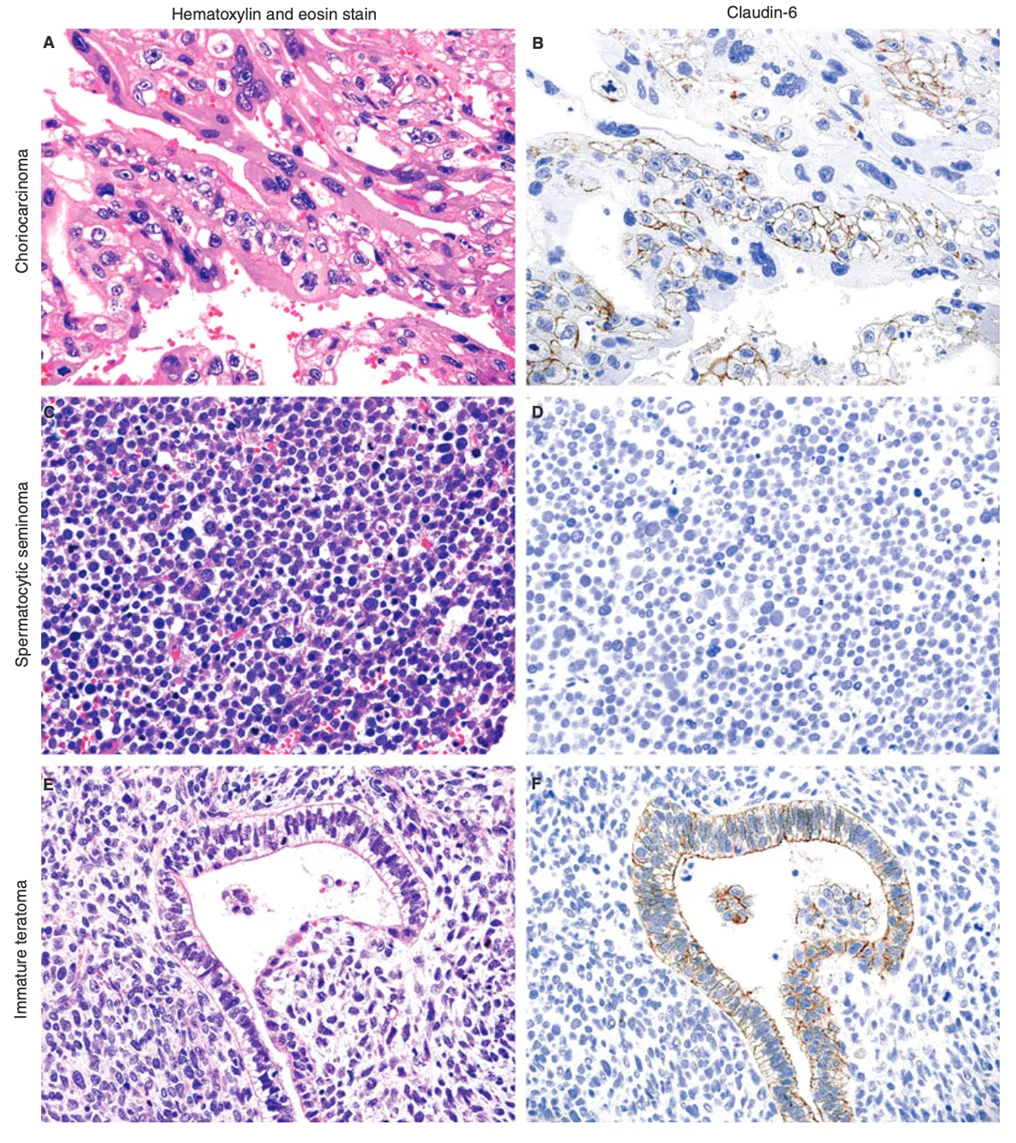
图5: CLDN6在不同生殖细胞癌中的表达[2]
绒毛膜癌(A,B)、精原细胞瘤(C,D)和未成熟畸胎瘤(E,F)的H&E色及claudin -6免疫组化染色。Claudin-6染色几乎存在于所有的单核滋养细胞中,但在绒毛膜癌的合胞滋养细胞中不存在(A,B)。精原细胞瘤未见claudin-6染色(C,D)。在未成熟畸胎瘤中,未成熟腺细胞中检测到弱至中度的claudin-6染色,而周围未成熟基质细胞中未检测到claudin-6染色(E,F)。
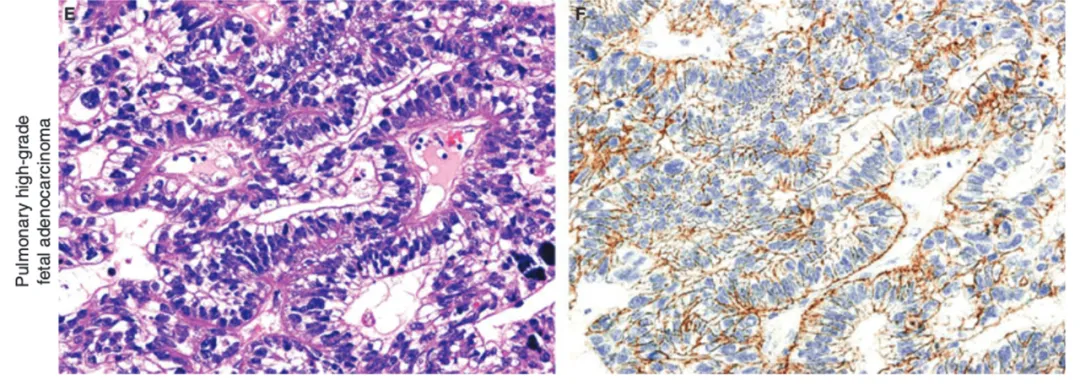
图6:CLDN6在高级别胎儿肺腺癌中的表达[2]
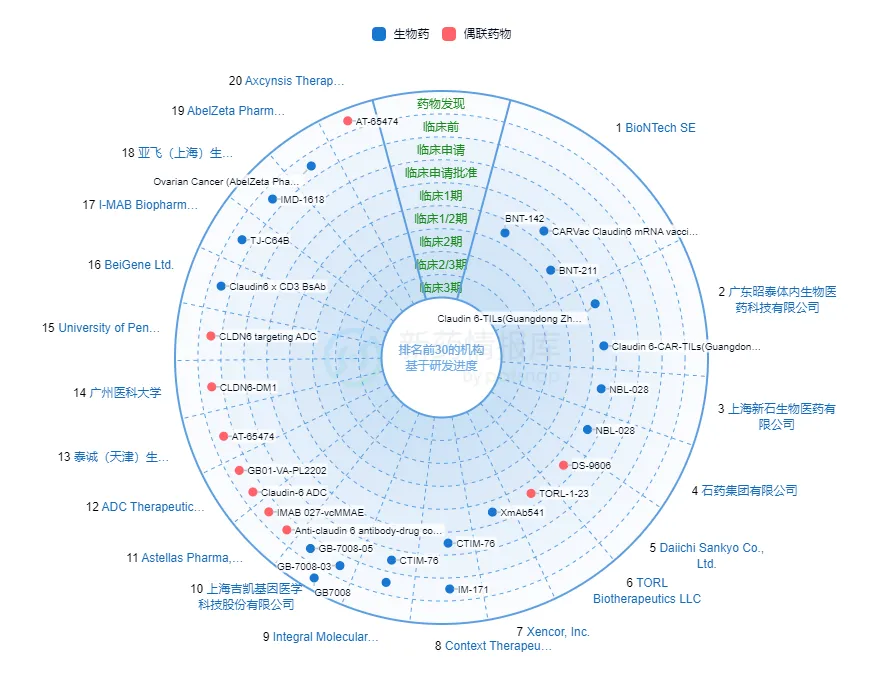
图7: 全球靶向CLDN6的药物研究进展
CLDN6作为一种细胞与细胞间紧密连接(Tight Junction)蛋白,其在体内的异常表达对于肿瘤转移的发生起到了决定性的作用。因其仅在健康个体的胚胎发育时表达且不在成人组织中表达的特性,CLDN6是一种具有肿瘤特异性的蛋白质 [7] 。 它在多种实体肿瘤中表达,包括卵巢、子宫内膜、肺、胃和睾丸。 靶向C LDN6将减少患者在用药时因为靶向药物与健康组织上的受体结合而带来的副作用。 这使得CLDN6成为一个极具潜力的肿瘤治疗靶点。
参考文献
[1] Du, H., Yang, X., Fan, J. and Du, X. (2021). Claudin 6: Therapeutic prospects for tumours, and mechanisms of expression and regulation (Review). Molecular Medicine Reports, 24(3). doi:https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.12316.
[2] Kohmoto, T., Masuda, K., Shoda, K., Takahashi, R., Ujiro, S., Tange, S., Ichikawa, D., Otsuji, E. and Imoto, I. (2019). Claudin-6 is a single prognostic marker and functions as a tumor-promoting gene in a subgroup of intestinal type gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-019-01014-x.
[3] Lü, Y., Dang, Q., Yin, B., Su, X., Wang, L., Sun, J., Wei, J., Quan, C. and Li, Y. (2021). The Expression of CLDN6 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissue and the Effects of CLDN6 on Biological Phenotypes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Journal of Cancer, 12(18), pp.5454–5463. doi:https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.55727.
[4] Micke, P., Sofia, J., Edlund, K., Lohr, M., Jirström, K., Berglund, A., Johan Botling, Jörg Rahnenfuehrer, Millaray Marincevic, Fredrik Pontén, Ekman, S., Hengstler, J.G., Wöll, S., Uğur Şahin and Özlem Türeci (2014). Aberrantly activated claudin 6 and 18.2 as potential therapy targets in non‐small‐cell lung cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 135(9), pp.2206–2214. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28857.
[5] Ushiku, T., Shinozaki-Ushiku, A., Maeda, D., Morita, S. and Fukayama, M. (2012). Distinct expression pattern of claudin-6, a primitive phenotypic tight junction molecule, in germ cell tumours and visceral carcinomas. Histopathology, 61(6), pp.1043–1056. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2012.04314.x.
[6] Yu, S., Zhang, Y., Li, Q., Zhang, Z., Zhao, G. and Xu, J. (2019). CLDN6 promotes tumor progression through the YAP1-snail1 axis in gastric cancer. Cell Death & Disease, 10(12). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2168-y.
[7] Zhang, C., Guo, C., Li, Y., Liu, K., Zhao, Q. and Ouyang, L. (2021). Identification of Claudin-6 as a Molecular Biomarker in Pan-Cancer Through Multiple Omics Integrative Analysis. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.726656.
央视《匠心》栏目视角看迈杰转化医学